- Return to book
- Review this book
- About the author
- Introduction
- 1. C++ programming language
- 2. C++ basics
- 3. Flow control
- 4. Functions
- 5. Arrays and Strings
- 6. Pointers
- 7. Classes and structs
- 8. Object-Oriented Programming
- 9. Memory Management
- 10. Advanced topics I
- 11. Advanced topics II
- 12. Exercises: miscellaneous
- 13. GDB
Instances
An instance is an occurrence of a class. Different instances can have their own set of values in their fields. If we continue the example shown before:
class MITStudent {
public:
char *name;
int studentID;
};
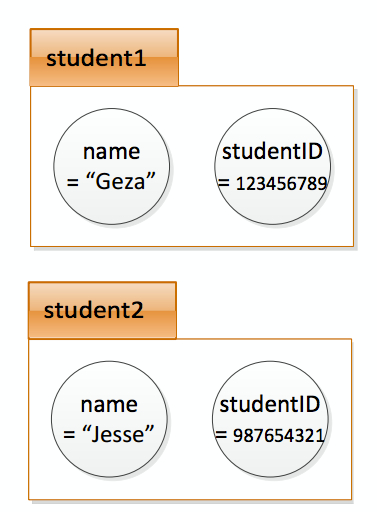
Now, if you wanted to represent 2 different students (who can have different names and IDs), you would use 2 instances of MITStudent. So we define 2 instances of MITStudent: one called student1, the other called student2.
class MITStudent {
public:
char *name;
int studentID;
};
int main() {
MITStudent student1;
MITStudent student2;
}
To access fields of instances, use
variable.fieldName.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class MITStudent {
public:
char *name;
int studentID;
};
int main() {
MITStudent student1;
MITStudent student2;
student1.name = "Geza";
student1.studentID = 123456789;
student2.name = "Jesse";
student2.studentID = 987654321;
cout << "student1 name is" << student1.name << endl;
cout << "student1 id is" << student1.studentID << endl;
cout << "student2 name is" << student2.name << endl;
cout << "student2 id is" << student2.studentID << endl;
return 0;
}