- Return to book
- Review this book
- About the author
- Introduction
- 1. Introduction to the UNIX Operating System
- 2. Tutorial One
- 3. Tutorial Two
- 4. Tutorial Three
- 5. Tutorial Four
- 6. Tutorial Five
- 7. Tutorial Six
- 8. Tutorial Seven
- 9. Tutorial Eight
- 10. Tutorial Nine
- 11. Tutorial Ten
- 12. Annex I: basic commands
- 13. Annex II: First steps with Erle
- 14. Annex III: Network connection with Erle
Other useful Unix commands
df
The df command reports on the space left on the file system. For example, to find out how much space is left on the fileserver, type
df .
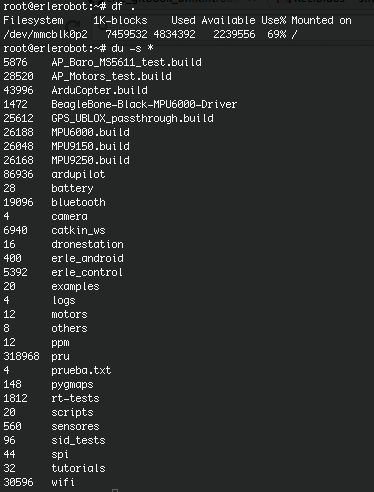
du
The du command outputs the number of kilobyes used by each subdirectory. If you want to find out which directory has the most files. In your home-directory, type
du -s *
The -s flag will display only a summary (total size) and the * means all files and directories.
working with erlerobot:
gzip
This reduces the size of a file, thus freeing valuable disk space. For example, type
ls -l science.txt
and note the size of the file using ls -l. Then to compress science.txt, type
gzip science.txt
This will compress the file and place it in a file called science.txt.gz
To see the change in size, typels -l again.
To expand the file, use the gunzip command.
gunzip science.txt.gz
zcat
zcat will read gzipped files without needing to uncompress them first.
zcat science.txt.gz
If the text scrolls too fast for you, pipe the output though less .
zcat science.txt.gz | less
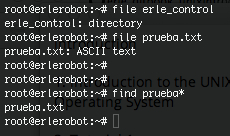
file
file classifies the named files according to the type of data they contain, for example ascii (text), pictures, compressed data, etc.. To report on all files in your home directory, type
file *
diff
This command compares the contents of two files and displays the differences. Suppose you have a file called file1 and you edit some part of it and save it as file2. To see the differences type
diff file1 file2
Lines beginning with a < denotes file1, while lines beginning with a > denotes file2.
find
This searches through the directories for files and directories with a given name, date, size, or any other attribute you care to specify. It is a simple command but with many options - you can read the manual by typing man find.
To search for all files with the extention .txt, starting at the current directory (.) and working through all sub-directories, then printing the name of the file to the screen, type
find . -name "*.txt" -print
To find files over 1Mb in size, and display the result as a long listing, type
find . -size +1M -ls
working with erlerobot:
history
The C shell keeps an ordered list of all the commands that you have entered. Each command is given a number according to the order it was entered.
history (show command history list)
If you are using the C shell, you can use the exclamation character (!) to recall commands easily.
!! (recall last command)
!-3 (recall third most recent command)
!5 (recall 5th command in list)
!grep (recall last command starting with grep)
You can increase the size of the history buffer by typing
set history=100
By using the navigation keys on your keyboard (up, down) you can recall the previous commands.
You can also use the recursive search. If you type ^R ([control +R]) and afterward the letter c, the shell shows you the previus commands beginning with c.
Shutdown
If you want to turn off a Linux machine, type:
shutdown -h now
bc
The command bc open an arbitrary precision calculator language. To use it type:
bc
(a text should appear on yout screen)
7*2
(the result should be 14)
quit (you get out of the calculator)
Another possibility of evaluating this is typing:
echo '7*2' | bc -l
Also, it can evaluate expressions like exp1 < exp2
returning a 1 if it is true and a 0 if it is false.
For furtherinformation type:
man bc