GCS_mavlink.pde
GCS_Mavlink.pde
Link to the code:GCS_Mavlink.pde
MavLink is a communication protocol for MAV (Micro Aerial Vehicles) that has nowadays been extended to all kind of drones (both aerial and terrestrial).
A Ground Control station (GCS) is a land- or sea-based control center that provides the facilities for human control of unmanned vehicles in the air or in space.When talking about a rover it can be as simple as a remote control device.
In this file the MavLink protocol is implemented and adapted to a rover.Remote control methods and sensors (rate control, attitude stabilization, yaw, altitud...) are enabled.
// default sensors are present and healthy: gyro, accelerometer, rate_control, attitude_stabilization, yaw_position, altitude control, x/y position control, motor_control
#define MAVLINK_SENSOR_PRESENT_DEFAULT (MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_3D_GYRO | MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_3D_ACCEL | MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_ANGULAR_RATE_CONTROL | MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_ATTITUDE_STABILIZATION | MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_YAW_POSITION | MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_XY_POSITION_CONTROL | MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_MOTOR_OUTPUTS | MAV_SYS_STATUS_AHRS)
// use this to prevent recursion during sensor init
static bool in_mavlink_delay;
// true if we are out of time in our event timeslice
static bool gcs_out_of_time;
// check if a message will fit in the payload space available
#define CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(id) if (payload_space < MAVLINK_MSG_ID_## id ##_LEN) return false
...
Defines some variables and stablish the default configuration for sensors.
You can fingure out what each sensor configuration does here as part of GCS_MAVLink/include/mavlink/v1.0/common/common.hfile.
/*
* !!NOTE!!
*
* the use of NOINLINE separate functions for each message type avoids
* a compiler bug in gcc that would cause it to use far more stack
* space than is needed. Without the NOINLINE we use the sum of the
* stack needed for each message type. Please be careful to follow the
* pattern below when adding any new messages
*/
static NOINLINE void send_heartbeat(mavlink_channel_t chan)
{
uint8_t base_mode = MAV_MODE_FLAG_CUSTOM_MODE_ENABLED;
uint8_t system_status = MAV_STATE_ACTIVE;
uint32_t custom_mode = control_mode;
if (failsafe.triggered != 0) {
system_status = MAV_STATE_CRITICAL;
}
...
Stablishes the system status to ACTIVE and the control mode. Checks if the failsafe event is set (it means triggered() returns something different from 0). In case the failsafe event is set the status is changed to CRITICAL.
...
// work out the base_mode. This value is not very useful
// for APM, but we calculate it as best we can so a generic
// MAVLink enabled ground station can work out something about
// what the MAV is up to. The actual bit values are highly
// ambiguous for most of the APM flight modes. In practice, you
// only get useful information from the custom_mode, which maps to
// the APM flight mode and has a well defined meaning in the
// ArduPlane documentation
switch (control_mode) {
case MANUAL:
case LEARNING:
case STEERING:
base_mode = MAV_MODE_FLAG_MANUAL_INPUT_ENABLED;
break;
case AUTO:
case RTL:
case GUIDED:
base_mode = MAV_MODE_FLAG_GUIDED_ENABLED;
// note that MAV_MODE_FLAG_AUTO_ENABLED does not match what
// APM does in any mode, as that is defined as "system finds its own goal
// positions", which APM does not currently do
break;
case INITIALISING:
system_status = MAV_STATE_CALIBRATING;
break;
case HOLD:
system_status = 0;
break;
}
...
Depending on the control_mode some variables are defined.The MAV_MODE_GLAG are defined as part of PX4 firmware, you can find the definitions here.
MAV_MODE_FLAG_GUIDED_ENABLED:guided mode enabled, system flies MISSIONs / mission items
MAV_MODE_FLAG_AUTO_ENABLED:autonomous mode enabled, system finds its own goal positions. Guided flag can be set or not, depends on the actual implementation.
At ardupilot/libraries/GCS_MAVLink/include/mavlink/v1.0 you can find all these identifiers.
#if ENABLE_STICK_MIXING==ENABLED
if (control_mode != INITIALISING) {
// all modes except INITIALISING have some form of manual
// override if stick mixing is enabled
base_mode |= MAV_MODE_FLAG_MANUAL_INPUT_ENABLED;
}
#endif
...
Remote control input is (MAV_MODE_FLAG_MANUAL_INPUT_ENABLED), in case the control mode is not INITIALISING.
#if HIL_MODE != HIL_MODE_DISABLED
base_mode |= MAV_MODE_FLAG_HIL_ENABLED;
#endif
// we are armed if we are not initialising
if (control_mode != INITIALISING && ahrs.get_armed()) {
base_mode |= MAV_MODE_FLAG_SAFETY_ARMED;
}
// indicate we have set a custom mode
base_mode |= MAV_MODE_FLAG_CUSTOM_MODE_ENABLED;
mavlink_msg_heartbeat_send(
chan,
MAV_TYPE_GROUND_ROVER,
MAV_AUTOPILOT_ARDUPILOTMEGA,
base_mode,
custom_mode,
system_status);
}
...
The Hil mode is defined in the APMrover2/config.h.As mentioned before, the simulation Hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) is a technique used for the development and testing of complex embedded systems in real time.
First this code checks if HIL is enabled in some way.
MAV_MODE_FLAG_HIL_ENABLED also enables hardware in the loop simulation (all motors / actuators are blocked, but internal software is full operational).
After that MAV_MODE_FLAG_SAFETY_ARMED sets MAV safety to armed. Motors are enabled / running / can start, that means: "Ready to fly".
Then MAV_MODE_FLAG_CUSTOM_MODE_ENABLED is used to set a custom mode(a bitfield for use for autopilot-specific flags).
You can find the implementation of mavlink_msg_heartbeat_sendhere, for sending a heartbeat message.
NOTE- mavlink_msg... can be found at /GCS_MAVLink/include/mavlink/v1.0/ardupilotmega or at /GCS_MAVLink/include/mavlink/v1.0/common.
static NOINLINE void send_attitude(mavlink_channel_t chan)
{
Vector3f omega = ahrs.get_gyro();
mavlink_msg_attitude_send(
chan,
millis(),
ahrs.roll,
ahrs.pitch,
ahrs.yaw,
omega.x,
omega.y,
omega.z);
}
...
This function send_attitude sends a message containing the attitude variables' values:
get_gyro()return a smoothed and corrected gyro vector.
mavlink_msg_attitude_sendimplemented here send an attitude message:- (x,y,z) for position of the certer of gravity respect to a non-inertial system.
- (roll,pitch,yaw) for orientation relative to a body- fixed system (inertial) .
Note that the position of a body is perfectly determined with both the position of a point (GC) and the rotated angles relative to a given position.
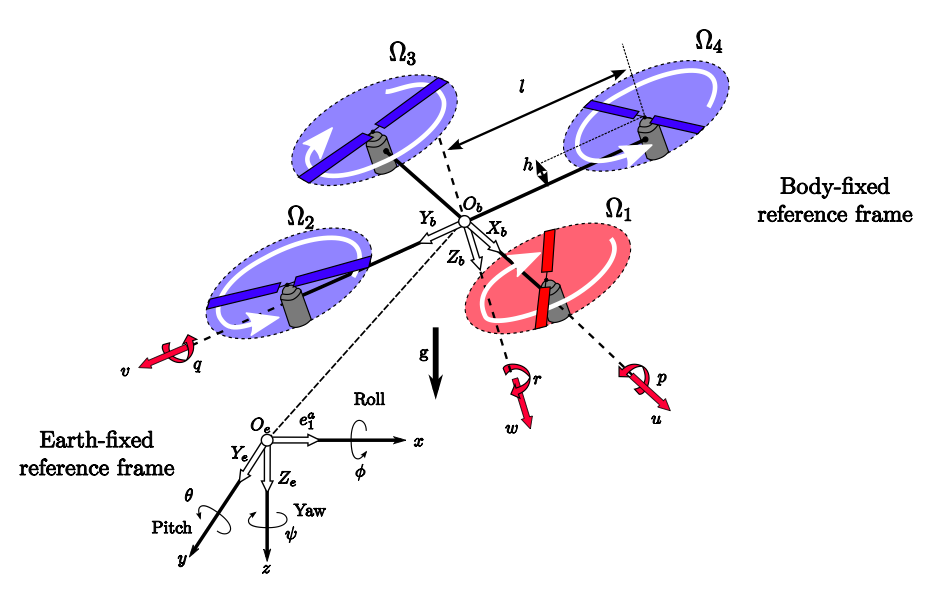
static NOINLINE void send_extended_status1(mavlink_channel_t chan)
{
uint32_t control_sensors_present;
uint32_t control_sensors_enabled;
uint32_t control_sensors_health;
// default sensors present
control_sensors_present = MAVLINK_SENSOR_PRESENT_DEFAULT;
...
This initilized contol_sensors_present to the default sensors stablished in the firts line of this code.
...
// first what sensors/controllers we have
if (g.compass_enabled) {
control_sensors_present |= MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_3D_MAG; // compass present
}
if (gps.status() > AP_GPS::NO_GPS) {
control_sensors_present |= MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_GPS;
}
...
Enables the GPS sensor and the Magnetometer sensor if they exist.
...
// all present sensors enabled by default except rate control, attitude stabilization, yaw, altitude, position control and motor output which we will set individually
control_sensors_enabled = control_sensors_present & (~MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_ANGULAR_RATE_CONTROL & ~MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_ATTITUDE_STABILIZATION & ~MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_YAW_POSITION & ~MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_XY_POSITION_CONTROL & ~MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_MOTOR_OUTPUTS);
switch (control_mode) {
case MANUAL:
case HOLD:
break;
case LEARNING:
case STEERING:
control_sensors_enabled |= MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_ANGULAR_RATE_CONTROL; // 3D angular rate control
control_sensors_enabled |= MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_ATTITUDE_STABILIZATION; // attitude stabilisation
break;
case AUTO:
case RTL:
case GUIDED:
control_sensors_enabled |= MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_ANGULAR_RATE_CONTROL; // 3D angular rate control
control_sensors_enabled |= MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_ATTITUDE_STABILIZATION; // attitude stabilisation
control_sensors_enabled |= MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_YAW_POSITION; // yaw position
control_sensors_enabled |= MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_XY_POSITION_CONTROL; // X/Y position control
control_sensors_enabled |= MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_MOTOR_OUTPUTS; // motor control
break;
case INITIALISING:
break;
}
...
Depending on the control_mode input different sensors are enabled.
...
// default to all healthy except compass and gps which we set individually
control_sensors_health = control_sensors_present & (~MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_3D_MAG & ~MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_GPS);
if (g.compass_enabled && compass.healthy(0) && ahrs.use_compass()) {
control_sensors_health |= MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_3D_MAG;
}
if (gps.status() >= AP_GPS::GPS_OK_FIX_3D) {
control_sensors_health |= MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_GPS;
}
if (!ins.healthy()) {
control_sensors_health &= ~(MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_3D_GYRO | MAV_SYS_STATUS_SENSOR_3D_ACCEL);
}
if (!ahrs.healthy()) {
// AHRS subsystem is unhealthy
control_sensors_health &= ~MAV_SYS_STATUS_AHRS;
}
int16_t battery_current = -1;
int8_t battery_remaining = -1;
if (battery.monitoring() == AP_BATT_MONITOR_VOLTAGE_AND_CURRENT) {
battery_remaining = battery.capacity_remaining_pct();
battery_current = battery.current_amps() * 100;
}
...
This slice of code check if a device is connected and enabled in a healthy way.Depending on this initialize the corresponding sensor.That means, this slice is a health controller.
For example:
ahrs.healthy() checks if the AHRS subsystem is healthy (boolean function). If it is unhealthy MAV_SYS_STATUS_AHRSis called to find out the AHRS subsystem health.
...
mavlink_msg_sys_status_send(
chan,
control_sensors_present,
control_sensors_enabled,
control_sensors_health,
(uint16_t)(scheduler.load_average(20000) * 1000),
battery.voltage() * 1000, // mV
battery_current, // in 10mA units
battery_remaining, // in %
0, // comm drops %,
0, // comm drops in pkts,
0, 0, 0, 0);
}
...
mavlink_msg_sys_status_sendimplemented here sends a message showing the status of the system. The message includes data about: which controllers and sensors are present, which are enabled, which controllers and sensors are operational or have an error...(Value of 0: not present. Value of 1: present).
static void NOINLINE send_location(mavlink_channel_t chan)
{
uint32_t fix_time;
// if we have a GPS fix, take the time as the last fix time. That
// allows us to correctly calculate velocities and extrapolate
// positions.
// If we don't have a GPS fix then we are dead reckoning, and will
// use the current boot time as the fix time.
if (gps.status() >= AP_GPS::GPS_OK_FIX_2D) {
fix_time = gps.last_fix_time_ms();
} else {
fix_time = millis();
}
const Vector3f &vel = gps.velocity();
mavlink_msg_global_position_int_send(
chan,
fix_time,
current_loc.lat, // in 1E7 degrees
current_loc.lng, // in 1E7 degrees
gps.location().alt * 10UL, // millimeters above sea level
(current_loc.alt - home.alt) * 10, // millimeters above ground
vel.x * 100, // X speed cm/s (+ve North)
vel.y * 100, // Y speed cm/s (+ve East)
vel.z * -100, // Z speed cm/s (+ve up)
ahrs.yaw_sensor);
}
...
Some notes about the functions called.
last_fix_time_ms()returns the time we got our last fix in system milliseconds. This is used when calculating how far we might have moved since that fix.
gps.velocity()returns 3D velocity in NED format.
location()returns the location of last fix.
yaw_sensoris anAP_InertialSensorexported to AHRS, which can be defined as, a gyroscopic device that measures a vehicle’s angular velocity around its vertical axis.current_locis a Location instance. ALl location functions are stored in [AP_Math] The information returned by all these functions is used when callingmavlink_msg_global_position_int_send, implemented here.
static void NOINLINE send_nav_controller_output(mavlink_channel_t chan)
{
mavlink_msg_nav_controller_output_send(
chan,
lateral_acceleration, // use nav_roll to hold demanded Y accel
gps.ground_speed() * ins.get_gyro().z, // use nav_pitch to hold actual Y accel
nav_controller->nav_bearing_cd() * 0.01f,
nav_controller->target_bearing_cd() * 0.01f,
wp_distance,
0,
groundspeed_error,
nav_controller->crosstrack_error());
}
...
send_nav_controller_output is implemented here and sends a nav_controller_output message.
The nav_controllermethods are defined in AP_Navigation.h:
nav_bearing_cd()returns the tracking bearing that the navigation controller is using in centi-degrees. This is used to display an arrow on ground stations showing the effect of the cross-tracking in the controller.target_bearing_cd()returns the target bearing in centi-degrees. This is the bearing from the vehicles current position to the target waypoint.crosstrack_error()returns the crosstrack error in meters. This is the distance inthe X-Y plane that we are off the desired track.
#if HIL_MODE != HIL_MODE_DISABLED
static void NOINLINE send_servo_out(mavlink_channel_t chan)
{
// normalized values scaled to -10000 to 10000
// This is used for HIL. Do not change without discussing with
// HIL maintainers
mavlink_msg_rc_channels_scaled_send(
chan,
millis(),
0, // port 0
10000 * channel_steer->norm_output(),
0,
10000 * channel_throttle->norm_output(),
0,
0,
0,
0,
0,
receiver_rssi);
}
#endif
...
If HIL_MODE is enabled send amavlink_msg_rc_channels_scaled_send implemented here.This send instructions to the corresponding channel, in this case: steer and throttle control channels.
static void NOINLINE send_radio_out(mavlink_channel_t chan)
{
#if HIL_MODE == HIL_MODE_DISABLED || HIL_SERVOS
mavlink_msg_servo_output_raw_send(
chan,
micros(),
0, // port
hal.rcout->read(0),
hal.rcout->read(1),
hal.rcout->read(2),
hal.rcout->read(3),
hal.rcout->read(4),
hal.rcout->read(5),
hal.rcout->read(6),
hal.rcout->read(7));
...
If the HIL_MODE is disabled calls mavlink_msg_servo_output_raw_send implemented here. Send a message to the servo output port for using RCOutput read() method to read back current output state, as either single channel or array of channels.
...
#else
mavlink_msg_servo_output_raw_send(
chan,
micros(),
0, // port
RC_Channel::rc_channel(0)->radio_out,
RC_Channel::rc_channel(1)->radio_out,
RC_Channel::rc_channel(2)->radio_out,
RC_Channel::rc_channel(3)->radio_out,
RC_Channel::rc_channel(4)->radio_out,
RC_Channel::rc_channel(5)->radio_out,
RC_Channel::rc_channel(6)->radio_out,
RC_Channel::rc_channel(7)->radio_out);
#endif
}
...
If HIL_MODE is enabled uses RC_Channel manager.
static void NOINLINE send_vfr_hud(mavlink_channel_t chan)
{
mavlink_msg_vfr_hud_send(
chan,
gps.ground_speed(),
gps.ground_speed(),
(ahrs.yaw_sensor / 100) % 360,
(uint16_t)(100 * fabsf(channel_throttle->norm_output())),
current_loc.alt / 100.0,
0);
}
...
mavlink_msg_vrf_hud_send implemented here send information about: Current airspeed in m/s and ground speed in m/s,
current throttle setting, current altitude (MSL)...
This information is get through gps.ground_speed(), ahrs.yaw_sensor...)
// report simulator state
static void NOINLINE send_simstate(mavlink_channel_t chan)
{
#if CONFIG_HAL_BOARD == HAL_BOARD_AVR_SITL
sitl.simstate_send(chan);
#endif
}
...
void simstate_send(mavlink_channel_t chan);for reporting the state.Implemented here.
static void NOINLINE send_hwstatus(mavlink_channel_t chan)
{
mavlink_msg_hwstatus_send(
chan,
hal.analogin->board_voltage()*1000,
hal.i2c->lockup_count());
}
...
mavlink_msg_hwstatus_send implemented here is used to sent Vcc- board voltage (mV) and I2Cerr- I2C error count.
The function definition take care about the arguments passed to it) is :static inline void mavlink_msg_hwstatus_send(mavlink_channel_t chan, uint16_t Vcc, uint8_t I2Cerr)
static void NOINLINE send_rangefinder(mavlink_channel_t chan)
{
if (!sonar.healthy()) {
// no sonar to report
return;
}
/*
report smaller distance of two sonars if more than one enabled
*/
float distance_cm, voltage;
if (!sonar.healthy(1)) {
distance_cm = sonar.distance_cm(0);
voltage = sonar.voltage_mv(0) * 0.001f;
} else {
float dist1 = sonar.distance_cm(0);
float dist2 = sonar.distance_cm(1);
if (dist1 <= dist2) {
distance_cm = dist1;
voltage = sonar.voltage_mv(0) * 0.001f;
} else {
distance_cm = dist2;
voltage = sonar.voltage_mv(1) * 0.001f;
}
}
mavlink_msg_rangefinder_send(
chan,
distance_cm * 0.01f,
voltage);
}
...
Using sonar methods implemented here report smaller distance of two sonars if more than one enabled.
Then using mavlink_msg_rangefinder_send, implemented here, sent a message with the distance in meters and a raw voltage if available(zero otherwise).
static void NOINLINE send_current_waypoint(mavlink_channel_t chan)
{
mavlink_msg_mission_current_send(chan, mission.get_current_nav_index());
}
...
mavlink_msg_mission_current_send implemented here for sending a mission_current message, which reports the mission command in Mavlink.For this aim get_current_nav_index is used: get_current_nav_index returns the current "navigation" command index. Note that this will return 0 if there is no command. This is used in MAVLink reporting of the mission command.
static void NOINLINE send_statustext(mavlink_channel_t chan)
{
mavlink_statustext_t *s = &gcs[chan-MAVLINK_COMM_0].pending_status;
mavlink_msg_statustext_send(
chan,
s->severity,
s->text);
}
...
This code sends a message as implemented here.
severityof status. Relies on the definitions within RFC-5424(RFC 5424 is The Syslog Protocol).
- Status
textmessage, without null termination character.
// are we still delaying telemetry to try to avoid Xbee bricking?
static bool telemetry_delayed(mavlink_channel_t chan)
{
uint32_t tnow = millis() >> 10;
if (tnow > (uint32_t)g.telem_delay) {
return false;
}
if (chan == MAVLINK_COMM_0 && hal.gpio->usb_connected()) {
// this is USB telemetry, so won't be an Xbee
return false;
}
// we're either on the 2nd UART, or no USB cable is connected
// we need to delay telemetry by the TELEM_DELAY time
return true;
}
...
Telemetry is the highly automated communications process by which measurements are made and other data collected at remote or inaccessible points and transmitted to receiving equipment for monitoring.
Now we try to delay telemetry using telem_delay defined here.
Notice, that it is checked if the usb is connected or not, with usb_connected , which return true if USB cable is connected .
// try to send a message, return false if it won't fit in the serial tx buffer
bool GCS_MAVLINK::try_send_message(enum ap_message id)
{
int16_t payload_space = comm_get_txspace(chan) - MAVLINK_NUM_NON_PAYLOAD_BYTES;
if (telemetry_delayed(chan)) {
return false;
}
// if we don't have at least 1ms remaining before the main loop
// wants to fire then don't send a mavlink message. We want to
// prioritise the main flight control loop over communications
if (!in_mavlink_delay && scheduler.time_available_usec() < 1200) {
gcs_out_of_time = true;
return false;
}
...
This slice of code checks if we j¡have remaining time for sending a message.
switch (id) {
case MSG_HEARTBEAT:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(HEARTBEAT);
gcs[chan-MAVLINK_COMM_0].last_heartbeat_time = hal.scheduler->millis();
send_heartbeat(chan);
return true;
case MSG_EXTENDED_STATUS1:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(SYS_STATUS);
send_extended_status1(chan);
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(POWER_STATUS);
gcs[chan-MAVLINK_COMM_0].send_power_status();
break;
case MSG_EXTENDED_STATUS2:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(MEMINFO);
gcs[chan-MAVLINK_COMM_0].send_meminfo();
break;
case MSG_ATTITUDE:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(ATTITUDE);
send_attitude(chan);
break;
case MSG_LOCATION:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(GLOBAL_POSITION_INT);
send_location(chan);
break;
case MSG_NAV_CONTROLLER_OUTPUT:
if (control_mode != MANUAL) {
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(NAV_CONTROLLER_OUTPUT);
send_nav_controller_output(chan);
}
break;
case MSG_GPS_RAW:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(GPS_RAW_INT);
gcs[chan-MAVLINK_COMM_0].send_gps_raw(gps);
break;
case MSG_SYSTEM_TIME:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(SYSTEM_TIME);
gcs[chan-MAVLINK_COMM_0].send_system_time(gps);
break;
case MSG_SERVO_OUT:
#if HIL_MODE != HIL_MODE_DISABLED
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(RC_CHANNELS_SCALED);
send_servo_out(chan);
#endif
break;
case MSG_RADIO_IN:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(RC_CHANNELS_RAW);
gcs[chan-MAVLINK_COMM_0].send_radio_in(receiver_rssi);
break;
case MSG_RADIO_OUT:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(SERVO_OUTPUT_RAW);
send_radio_out(chan);
break;
case MSG_VFR_HUD:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(VFR_HUD);
send_vfr_hud(chan);
break;
case MSG_RAW_IMU1:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(RAW_IMU);
gcs[chan-MAVLINK_COMM_0].send_raw_imu(ins, compass);
break;
case MSG_RAW_IMU3:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(SENSOR_OFFSETS);
gcs[chan-MAVLINK_COMM_0].send_sensor_offsets(ins, compass, barometer);
break;
case MSG_CURRENT_WAYPOINT:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(MISSION_CURRENT);
send_current_waypoint(chan);
break;
case MSG_NEXT_PARAM:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(PARAM_VALUE);
gcs[chan-MAVLINK_COMM_0].queued_param_send();
break;
case MSG_NEXT_WAYPOINT:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(MISSION_REQUEST);
gcs[chan-MAVLINK_COMM_0].queued_waypoint_send();
break;
case MSG_STATUSTEXT:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(STATUSTEXT);
send_statustext(chan);
break;
case MSG_AHRS:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(AHRS);
gcs[chan-MAVLINK_COMM_0].send_ahrs(ahrs);
break;
case MSG_SIMSTATE:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(SIMSTATE);
send_simstate(chan);
break;
case MSG_HWSTATUS:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(HWSTATUS);
send_hwstatus(chan);
break;
case MSG_RANGEFINDER:
CHECK_PAYLOAD_SIZE(RANGEFINDER);
send_rangefinder(chan);
break;
case MSG_RAW_IMU2:
case MSG_LIMITS_STATUS:
case MSG_FENCE_STATUS:
case MSG_WIND:
// unused
break;
case MSG_RETRY_DEFERRED:
break; // just here to prevent a warning
}
return true;
}
...
This case involve MSG_ varibles. To ensure we never block on sending MAVLink messages
each MSG_ is keept to a single MAVLink message.
For example: In case MSG_ATTITUDEthe previously defined function send_attitude is called.
All the options in this case are used in a similar way.
/*
default stream rates to 1Hz
*/
const AP_Param::GroupInfo GCS_MAVLINK::var_info[] PROGMEM = {
// @Param: RAW_SENS
// @DisplayName: Raw sensor stream rate
// @Description: Raw sensor stream rate to ground station
// @Units: Hz
// @Range: 0 10
// @Increment: 1
// @User: Advanced
AP_GROUPINFO("RAW_SENS", 0, GCS_MAVLINK, streamRates[0], 1),
...
The GroupInfo structure is passed by the main
program in setup() to give information on how variables are named and their location in memory. It is defined here.
This codes pass stream rates to the GCS.In this first case about the raw sensor. In the same way does it for the following:
// @Param: EXT_STAT
// @DisplayName: Extended status stream rate to ground station
// @Description: Extended status stream rate to ground station
// @Units: Hz
// @Range: 0 10
// @Increment: 1
// @User: Advanced
AP_GROUPINFO("EXT_STAT", 1, GCS_MAVLINK, streamRates[1], 1),
// @Param: RC_CHAN
// @DisplayName: RC Channel stream rate to ground station
// @Description: RC Channel stream rate to ground station
// @Units: Hz
// @Range: 0 10
// @Increment: 1
// @User: Advanced
AP_GROUPINFO("RC_CHAN", 2, GCS_MAVLINK, streamRates[2], 1),
// @Param: RAW_CTRL
// @DisplayName: Raw Control stream rate to ground station
// @Description: Raw Control stream rate to ground station
// @Units: Hz
// @Range: 0 10
// @Increment: 1
// @User: Advanced
AP_GROUPINFO("RAW_CTRL", 3, GCS_MAVLINK, streamRates[3], 1),
// @Param: POSITION
// @DisplayName: Position stream rate to ground station
// @Description: Position stream rate to ground station
// @Units: Hz
// @Range: 0 10
// @Increment: 1
// @User: Advanced
AP_GROUPINFO("POSITION", 4, GCS_MAVLINK, streamRates[4], 1),
// @Param: EXTRA1
// @DisplayName: Extra data type 1 stream rate to ground station
// @Description: Extra data type 1 stream rate to ground station
// @Units: Hz
// @Range: 0 10
// @Increment: 1
// @User: Advanced
AP_GROUPINFO("EXTRA1", 5, GCS_MAVLINK, streamRates[5], 1),
// @Param: EXTRA2
// @DisplayName: Extra data type 2 stream rate to ground station
// @Description: Extra data type 2 stream rate to ground station
// @Units: Hz
// @Range: 0 10
// @Increment: 1
// @User: Advanced
AP_GROUPINFO("EXTRA2", 6, GCS_MAVLINK, streamRates[6], 1),
// @Param: EXTRA3
// @DisplayName: Extra data type 3 stream rate to ground station
// @Description: Extra data type 3 stream rate to ground station
// @Units: Hz
// @Range: 0 10
// @Increment: 1
// @User: Advanced
AP_GROUPINFO("EXTRA3", 7, GCS_MAVLINK, streamRates[7], 1),
// @Param: PARAMS
// @DisplayName: Parameter stream rate to ground station
// @Description: Parameter stream rate to ground station
// @Units: Hz
// @Range: 0 10
// @Increment: 1
// @User: Advanced
AP_GROUPINFO("PARAMS", 8, GCS_MAVLINK, streamRates[8], 10),
AP_GROUPEND
};
...
AS you can see the scheme is similar to the explained one.
// see if we should send a stream now. Called at 50Hz
bool GCS_MAVLINK::stream_trigger(enum streams stream_num)
{
if (stream_num >= NUM_STREAMS) {
return false;
}
float rate = (uint8_t)streamRates[stream_num].get();
// send at a much lower rate while handling waypoints and
// parameter sends
if ((stream_num != STREAM_PARAMS) &&
(waypoint_receiving || _queued_parameter != NULL)) {
rate *= 0.25;
}
if (rate <= 0) {
return false;
}
if (stream_ticks[stream_num] == 0) {
// we're triggering now, setup the next trigger point
if (rate > 50) {
rate = 50;
}
stream_ticks[stream_num] = (50 / rate) + stream_slowdown;
return true;
}
// count down at 50Hz
stream_ticks[stream_num]--;
return false;
}
...
The stream parameters are defined in GCS.h
This slice of code checks if the stream parameters are set in a such a way that a new stream should be sent.
void
GCS_MAVLINK::data_stream_send(void)
{
gcs_out_of_time = false;
if (!in_mavlink_delay) {
handle_log_send(DataFlash);
}
if (_queued_parameter != NULL) {
if (streamRates[STREAM_PARAMS].get() <= 0) {
streamRates[STREAM_PARAMS].set(10);
}
if (stream_trigger(STREAM_PARAMS)) {
send_message(MSG_NEXT_PARAM);
}
}
if (gcs_out_of_time) return;
if (in_mavlink_delay) {
#if HIL_MODE != HIL_MODE_DISABLED
// in HIL we need to keep sending servo values to ensure
// the simulator doesn't pause, otherwise our sensor
// calibration could stall
if (stream_trigger(STREAM_RAW_CONTROLLER)) {
send_message(MSG_SERVO_OUT);
}
if (stream_trigger(STREAM_RC_CHANNELS)) {
send_message(MSG_RADIO_OUT);
}
#endif
// don't send any other stream types while in the delay callback
return;
}
if (gcs_out_of_time) return;
if (stream_trigger(STREAM_RAW_SENSORS)) {
send_message(MSG_RAW_IMU1);
send_message(MSG_RAW_IMU3);
}
if (gcs_out_of_time) return;
if (stream_trigger(STREAM_EXTENDED_STATUS)) {
send_message(MSG_EXTENDED_STATUS1);
send_message(MSG_EXTENDED_STATUS2);
send_message(MSG_CURRENT_WAYPOINT);
send_message(MSG_GPS_RAW); // TODO - remove this message after location message is working
send_message(MSG_NAV_CONTROLLER_OUTPUT);
}
if (gcs_out_of_time) return;
if (stream_trigger(STREAM_POSITION)) {
// sent with GPS read
send_message(MSG_LOCATION);
}
if (gcs_out_of_time) return;
if (stream_trigger(STREAM_RAW_CONTROLLER)) {
send_message(MSG_SERVO_OUT);
}
if (gcs_out_of_time) return;
if (stream_trigger(STREAM_RC_CHANNELS)) {
send_message(MSG_RADIO_OUT);
send_message(MSG_RADIO_IN);
}
if (gcs_out_of_time) return;
if (stream_trigger(STREAM_EXTRA1)) {
send_message(MSG_ATTITUDE);
send_message(MSG_SIMSTATE);
}
if (gcs_out_of_time) return;
if (stream_trigger(STREAM_EXTRA2)) {
send_message(MSG_VFR_HUD);
}
if (gcs_out_of_time) return;
if (stream_trigger(STREAM_EXTRA3)) {
send_message(MSG_AHRS);
send_message(MSG_HWSTATUS);
send_message(MSG_RANGEFINDER);
send_message(MSG_SYSTEM_TIME);
}
}
...
Note: We have to set in_mavlink_delay to prevent logging while writing headers.
if stream triggerfills the passed parameter then send_messageis called. send messageis defined here and sends a message with a single numeric parameter. This may be a standalone message, or the GCS driver may have its own way of locating additional parameters to send.
void GCS_MAVLINK::handle_guided_request(AP_Mission::Mission_Command &cmd)
{
guided_WP = cmd.content.location;
set_mode(GUIDED);
// make any new wp uploaded instant (in case we are already in Guided mode)
set_guided_WP();
}
...
The quided_WP is updated to the location value. The set_modefuntion is implemented in system.pde including a case for selecting the control mode(Guided,manual,hold...).
The set_guided_WP()funtion defined in APMrover2/commands.h copy the new location value to wp.
void GCS_MAVLINK::handle_change_alt_request(AP_Mission::Mission_Command &cmd)
{
// nothing to do
}
...
This funtion is not implemented yet.
void GCS_MAVLINK::handleMessage(mavlink_message_t* msg)
{
switch (msg->msgid) {
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_REQUEST_DATA_STREAM:
{
handle_request_data_stream(msg, true);
break;
}
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_COMMAND_LONG:
{
// decode
mavlink_command_long_t packet;
mavlink_msg_command_long_decode(msg, &packet);
if (mavlink_check_target(packet.target_system, packet.target_component)) break;
uint8_t result = MAV_RESULT_UNSUPPORTED;
// do command
send_text_P(SEVERITY_LOW,PSTR("command received: "));
...
If MAVLINK_MSG_ID_REQUEST_DATA_STREAM, then handle_request_data_stream is called for sending a date request.
Then if MAVLINK_MSG_ID_COMMAND_LONG then mavlink_command_long_decode for decoding a command_long message into a struct.
switch(packet.command) {
case MAV_CMD_NAV_RETURN_TO_LAUNCH:
set_mode(RTL);
result = MAV_RESULT_ACCEPTED;
break;
...
Then if MAV_CMD_NAV_RETURN_TO_LAUNCHthe set_modeis changed to RTL(Register Transfer Level). RTL calls on do_RTL()
#if MOUNT == ENABLED
// Sets the region of interest (ROI) for the camera
case MAV_CMD_DO_SET_ROI:
Location roi_loc;
roi_loc.lat = (int32_t)(packet.param5 * 1.0e7f);
roi_loc.lng = (int32_t)(packet.param6 * 1.0e7f);
roi_loc.alt = (int32_t)(packet.param7 * 100.0f);
if (roi_loc.lat == 0 && roi_loc.lng == 0 && roi_loc.alt == 0) {
// switch off the camera tracking if enabled
if (camera_mount.get_mode() == MAV_MOUNT_MODE_GPS_POINT) {
camera_mount.set_mode_to_default();
}
} else {
// send the command to the camera mount
camera_mount.set_roi_cmd(&roi_loc);
}
result = MAV_RESULT_ACCEPTED;
break;
#endif
...
If the mount is enabled and MAV_CMD_DO_SET_ROI sets the region of interest (ROI) for a sensor set or the vehicle itself. This can then be used by the vehicles control system to control the vehicle attitude and the attitude of various sensors such as cameras. There are three cordinates needed to pin down the position.
case MAV_CMD_MISSION_START:
set_mode(AUTO);
result = MAV_RESULT_ACCEPTED;
break;
...
Case MAV_CMD_MISSION_START starts running a mission .first_itemis the first mission item to run; last_item is the last mission item to run (after this item is run, the mission ends).
case MAV_CMD_PREFLIGHT_CALIBRATION:
if (packet.param1 == 1 ||
packet.param2 == 1 ||
packet.param3 == 1) {
startup_INS_ground(true);
}
if (packet.param4 == 1) {
trim_radio();
}
result = MAV_RESULT_ACCEPTED;
break;
...
Case MAV_CMD_PREFLIGHT_CALIBRATION tiggers calibration. This command will be only accepted if in pre-flight mode. For example:
Gyro calibration: 0: no, 1: yes.
case MAV_CMD_PREFLIGHT_SET_SENSOR_OFFSETS:
if (packet.param1 == 2) {
// save first compass's offsets
compass.set_and_save_offsets(0, packet.param2, packet.param3, packet.param4);
result = MAV_RESULT_ACCEPTED;
}
if (packet.param1 == 5) {
// save secondary compass's offsets
compass.set_and_save_offsets(1, packet.param2, packet.param3, packet.param4);
result = MAV_RESULT_ACCEPTED;
}
break;
case MAV_CMD_DO_SET_MODE:
switch ((uint16_t)packet.param1) {
case MAV_MODE_MANUAL_ARMED:
case MAV_MODE_MANUAL_DISARMED:
set_mode(MANUAL);
result = MAV_RESULT_ACCEPTED;
break;
case MAV_MODE_AUTO_ARMED:
case MAV_MODE_AUTO_DISARMED:
set_mode(AUTO);
result = MAV_RESULT_ACCEPTED;
break;
case MAV_MODE_STABILIZE_DISARMED:
case MAV_MODE_STABILIZE_ARMED:
set_mode(LEARNING);
result = MAV_RESULT_ACCEPTED;
break;
default:
result = MAV_RESULT_UNSUPPORTED;
}
break;
case MAV_CMD_DO_SET_SERVO:
if (ServoRelayEvents.do_set_servo(packet.param1, packet.param2)) {
result = MAV_RESULT_ACCEPTED;
}
break;
case MAV_CMD_DO_REPEAT_SERVO:
if (ServoRelayEvents.do_repeat_servo(packet.param1, packet.param2, packet.param3, packet.param4*1000)) {
result = MAV_RESULT_ACCEPTED;
}
break;
case MAV_CMD_DO_SET_RELAY:
if (ServoRelayEvents.do_set_relay(packet.param1, packet.param2)) {
result = MAV_RESULT_ACCEPTED;
}
break;
case MAV_CMD_DO_REPEAT_RELAY:
if (ServoRelayEvents.do_repeat_relay(packet.param1, packet.param2, packet.param3*1000)) {
result = MAV_RESULT_ACCEPTED;
}
break;
case MAV_CMD_PREFLIGHT_REBOOT_SHUTDOWN:
if (packet.param1 == 1 || packet.param1 == 3) {
// when packet.param1 == 3 we reboot to hold in bootloader
hal.scheduler->reboot(packet.param1 == 3);
result = MAV_RESULT_ACCEPTED;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
mavlink_msg_command_ack_send_buf(
msg,
chan,
packet.command,
result);
break;
}
...
Till here there is a case implemented with MAV_CDM commands. Each case acts in a similar way to the above explained ones. Here you can find the function of each NAV_CDM.
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_SET_MODE:
{
// decode
mavlink_set_mode_t packet;
mavlink_msg_set_mode_decode(msg, &packet);
if (!(packet.base_mode & MAV_MODE_FLAG_CUSTOM_MODE_ENABLED)) {
// we ignore base_mode as there is no sane way to map
// from that bitmap to a APM flight mode. We rely on
// custom_mode instead.
break;
}
switch (packet.custom_mode) {
case MANUAL:
case HOLD:
case LEARNING:
case STEERING:
case AUTO:
case RTL:
set_mode((enum mode)packet.custom_mode);
break;
}
break;
}
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_MISSION_REQUEST_LIST:
{
handle_mission_request_list(mission, msg);
break;
}
// XXX read a WP from EEPROM and send it to the GCS
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_MISSION_REQUEST:
{
handle_mission_request(mission, msg);
break;
}
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_MISSION_ACK:
{
// not used
break;
}
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_PARAM_REQUEST_LIST:
{
handle_param_request_list(msg);
break;
}
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_PARAM_REQUEST_READ:
{
handle_param_request_read(msg);
break;
}
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_MISSION_CLEAR_ALL:
{
handle_mission_clear_all(mission, msg);
break;
}
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_MISSION_SET_CURRENT:
{
handle_mission_set_current(mission, msg);
break;
}
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_MISSION_COUNT:
{
handle_mission_count(mission, msg);
break;
}
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_MISSION_WRITE_PARTIAL_LIST:
{
handle_mission_write_partial_list(mission, msg);
break;
}
// XXX receive a WP from GCS and store in EEPROM
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_MISSION_ITEM:
{
handle_mission_item(msg, mission);
break;
}
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_PARAM_SET:
{
handle_param_set(msg, &DataFlash);
break;
}
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_RC_CHANNELS_OVERRIDE:
{
// allow override of RC channel values for HIL
// or for complete GCS control of switch position
// and RC PWM values.
if(msg->sysid != g.sysid_my_gcs) break; // Only accept control from our gcs
mavlink_rc_channels_override_t packet;
int16_t v[8];
mavlink_msg_rc_channels_override_decode(msg, &packet);
if (mavlink_check_target(packet.target_system,packet.target_component))
break;
v[0] = packet.chan1_raw;
v[1] = packet.chan2_raw;
v[2] = packet.chan3_raw;
v[3] = packet.chan4_raw;
v[4] = packet.chan5_raw;
v[5] = packet.chan6_raw;
v[6] = packet.chan7_raw;
v[7] = packet.chan8_raw;
hal.rcin->set_overrides(v, 8);
failsafe.rc_override_timer = millis();
failsafe_trigger(FAILSAFE_EVENT_RC, false);
break;
}
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_HEARTBEAT:
{
// We keep track of the last time we received a heartbeat from our GCS for failsafe purposes
if(msg->sysid != g.sysid_my_gcs) break;
last_heartbeat_ms = failsafe.rc_override_timer = millis();
failsafe_trigger(FAILSAFE_EVENT_GCS, false);
break;
}
#if HIL_MODE != HIL_MODE_DISABLED
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_HIL_STATE:
{
mavlink_hil_state_t packet;
mavlink_msg_hil_state_decode(msg, &packet);
// set gps hil sensor
Location loc;
loc.lat = packet.lat;
loc.lng = packet.lon;
loc.alt = packet.alt/10;
Vector3f vel(packet.vx, packet.vy, packet.vz);
vel *= 0.01f;
gps.setHIL(0, AP_GPS::GPS_OK_FIX_3D,
packet.time_usec/1000,
loc, vel, 10, 0, true);
// rad/sec
Vector3f gyros;
gyros.x = packet.rollspeed;
gyros.y = packet.pitchspeed;
gyros.z = packet.yawspeed;
// m/s/s
Vector3f accels;
accels.x = packet.xacc * (GRAVITY_MSS/1000.0f);
accels.y = packet.yacc * (GRAVITY_MSS/1000.0f);
accels.z = packet.zacc * (GRAVITY_MSS/1000.0f);
ins.set_gyro(0, gyros);
ins.set_accel(0, accels);
compass.setHIL(packet.roll, packet.pitch, packet.yaw);
break;
}
#endif // HIL_MODE
#if CAMERA == ENABLED
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_DIGICAM_CONFIGURE:
{
camera.configure_msg(msg);
break;
}
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_DIGICAM_CONTROL:
{
camera.control_msg(msg);
break;
}
#endif // CAMERA == ENABLED
#if MOUNT == ENABLED
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_MOUNT_CONFIGURE:
{
camera_mount.configure_msg(msg);
break;
}
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_MOUNT_CONTROL:
{
camera_mount.control_msg(msg);
break;
}
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_MOUNT_STATUS:
{
camera_mount.status_msg(msg, chan);
break;
}
#endif // MOUNT == ENABLED
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_RADIO:
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_RADIO_STATUS:
{
handle_radio_status(msg, DataFlash, should_log(MASK_LOG_PM));
break;
}
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_LOG_REQUEST_DATA:
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_LOG_ERASE:
in_log_download = true;
// fallthru
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_LOG_REQUEST_LIST:
if (!in_mavlink_delay) {
handle_log_message(msg, DataFlash);
}
break;
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_LOG_REQUEST_END:
in_log_download = false;
if (!in_mavlink_delay) {
handle_log_message(msg, DataFlash);
}
break;
#if HAL_CPU_CLASS > HAL_CPU_CLASS_16
case MAVLINK_MSG_ID_SERIAL_CONTROL:
handle_serial_control(msg, gps);
break;
#endif
default:
// forward unknown messages to the other link if there is one
for (uint8_t i=0; i<num_gcs; i++) {
if (gcs[i].initialised && i != (uint8_t)chan) {
mavlink_channel_t out_chan = (mavlink_channel_t)i;
// only forward if it would fit in the transmit buffer
if (comm_get_txspace(out_chan) > ((uint16_t)msg->len) + MAVLINK_NUM_NON_PAYLOAD_BYTES) {
_mavlink_resend_uart(out_chan, msg);
}
}
}
break;
} // end switch
} // end handle mavlink
...
Each of this MAVLINK_MSG_ID has its own .hfile, where it is defined.
For example MAVLINK_MSG_ID_MISSION_ACKis defined in mavlink_msg_mission_ack.h file.
Similarly, the rest are defined in their correponding .h file stored at /GCS_MAVLink/include/mavlink/v1.0/common.
/*
* a delay() callback that processes MAVLink packets. We set this as the
* callback in long running library initialisation routines to allow
* MAVLink to process packets while waiting for the initialisation to
* complete
*/
static void mavlink_delay_cb()
{
static uint32_t last_1hz, last_50hz, last_5s;
if (!gcs[0].initialised || in_mavlink_delay) return;
in_mavlink_delay = true;
uint32_t tnow = millis();
if (tnow - last_1hz > 1000) {
last_1hz = tnow;
gcs_send_message(MSG_HEARTBEAT);
gcs_send_message(MSG_EXTENDED_STATUS1);
}
if (tnow - last_50hz > 20) {
last_50hz = tnow;
gcs_update();
gcs_data_stream_send();
notify.update();
}
if (tnow - last_5s > 5000) {
last_5s = tnow;
gcs_send_text_P(SEVERITY_LOW, PSTR("Initialising APM..."));
}
check_usb_mux();
in_mavlink_delay = false;
}
...
This slice of code checks the delay in mavlink messages and makes the corresponding GCS updates.
/*
* send a message on both GCS links
*/
static void gcs_send_message(enum ap_message id)
{
for (uint8_t i=0; i<num_gcs; i++) {
if (gcs[i].initialised) {
gcs[i].send_message(id);
}
}
}
...
You can find de GCS_class methods definition here.Note that gcs is an instance of GCS_CLass:
initialised sets to true if this GCS link is active
bool initialised.
send_message sends a message with a single numeric parameter.
/*
* send data streams in the given rate range on both links
*/
static void gcs_data_stream_send(void)
{
for (uint8_t i=0; i<num_gcs; i++) {
if (gcs[i].initialised) {
gcs[i].data_stream_send();
}
}
}
...
Here the data_stream_send() send streams which match working frequency range.
/*
* look for incoming commands on the GCS links
*/
static void gcs_update(void)
{
for (uint8_t i=0; i<num_gcs; i++) {
if (gcs[i].initialised) {
#if CLI_ENABLED == ENABLED
gcs[i].update(run_cli);
#else
gcs[i].update(NULL);
#endif
}
}
}
...
The update method updates GCS state. This may involve checking for received bytes on the stream, or sending additional periodic messages.
static void gcs_send_text_P(gcs_severity severity, const prog_char_t *str)
{
for (uint8_t i=0; i<num_gcs; i++) {
if (gcs[i].initialised) {
gcs[i].send_text_P(severity, str);
}
}
#if LOGGING_ENABLED == ENABLED
DataFlash.Log_Write_Message_P(str);
#endif
}
...
The send_textmethod sends a text message.Where the parameters are: severity(a value describing the importance of the message) and str (the text to be sent).
/*
* send a low priority formatted message to the GCS
* only one fits in the queue, so if you send more than one before the
* last one gets into the serial buffer then the old one will be lost
*/
void gcs_send_text_fmt(const prog_char_t *fmt, ...)
{
va_list arg_list;
gcs[0].pending_status.severity = (uint8_t)SEVERITY_LOW;
va_start(arg_list, fmt);
hal.util->vsnprintf_P((char *)gcs[0].pending_status.text,
sizeof(gcs[0].pending_status.text), fmt, arg_list);
va_end(arg_list);
#if LOGGING_ENABLED == ENABLED
DataFlash.Log_Write_Message(gcs[0].pending_status.text);
#endif
gcs[0].send_message(MSG_STATUSTEXT);
for (uint8_t i=1; i<num_gcs; i++) {
if (gcs[i].initialised) {
gcs[i].pending_status = gcs[0].pending_status;
gcs[i].send_message(MSG_STATUSTEXT);
}
}
}
...
pending_statusrefers to message that are in the queue.This slice of code try to send this pending messages.
/**
retry any deferred messages
*/
static void gcs_retry_deferred(void)
{
gcs_send_message(MSG_RETRY_DEFERRED);
}
This funtions retries sending deferred messages.